VECTRA
VECTRA is a hybrid tri-core power synthesizer combining a virtual analog engine, an advanced wavetable engine and a procedural Forge engine with a bi-directional modulation system, modular effects and probability-based sequencing.
↗ audionerdz.net
Tri-Core Generation Engine
Overview
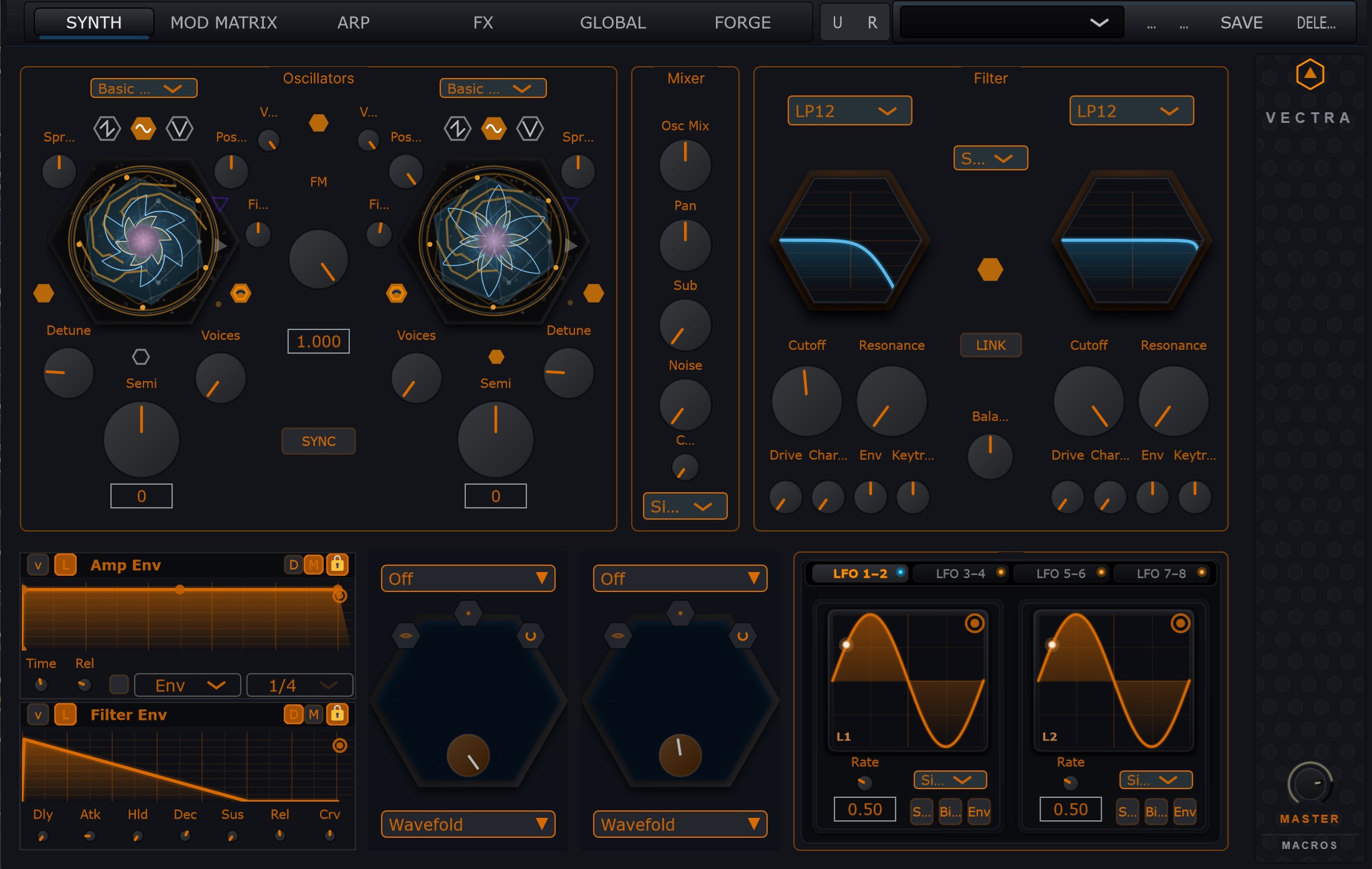
The VECTRA sound architecture is built around three complementary sources: a Virtual Analog
core, an Advanced Wave Core and the Forge vector/procedural engine.
Virtual Analog (VA) Core
The VA section provides classic, mix-ready oscillator behaviour.
- Oscillators: 2× high-precision PolyBLEP oscillators
- Waveforms: Saw, Square (PWM), Sine, Triangle
- Unison Engine: Up to 7-voice unison per oscillator with Spread & Detune
- Hard Sync: Master/Slave synchronization logic
- Sub-Oscillator: Dedicated sub (Sine / Square / Triangle) with direct routing
- Noise Generator: White noise with variable Color (Lowpass / Highpass tilt)
Advanced Wave Core (AWC)
High-resolution wavetable playback with destructive and real-time transformation.
- Playback: High-fidelity cubic interpolation (Catmull–Rom) or linear modes
Isotopic Mutator (Destructive Editing)
- Spectral FM – frequency modulation applied to the wavetable data structure
- Harmonic Content Morph (HCM) – spectral shifting and notch filtering of harmonics
- Wavefolding – mathematical folding of waveform geometry
- Spectral Modal Forge – resynthesis based on physical material properties
Real-Time Warp Modes
- Bend + / −
- Sync (Windowed)
- Mirror
- Pulse Width (PWM for wavetables)
- Quantize (bit-crush effect on phase)
- FM (phase modulation)
Forge – Vector Synthesis
Procedural wavetable engine with vector morphing.
- Architecture: 4-corner vector morphing engine
- Incubator: XY pad (IncubatorPanel) for blending 4 distinct “Parent” recipes
- Z-Morph: Third dimension scanning through generated wavetable frames
Procedural Aesir Algorithms (Parents)
- Aetheric Glass – physical modelling of struck solids
- Fractal FM – recursive modulation feedback loops
- Spectral Modal – material / stiffness / damping simulation
- Chaos Tamed Feedback – logistic map equation generation
- Golden Formant Choir – Phi-ratio formant spacing
- Crystalline Formant – noise-driven vocal textures
- Granular Hybrid – particle-based generation
- Phase Scatter – stochastic phase randomization
 alt="VECTRA Synth Panel" />
alt="VECTRA Synth Panel" />Twin-Turbine Filter Stack
Architecture
- Dual core: Filter 1 & Filter 2
- Routing: switchable Serial or Parallel
- Filter Balance: continuous blend between F1 and F2 outputs
- Stereo Link: options to offset cutoff / resonance per channel

 alt="Filter detail" />
alt="Filter detail" />Filter Models (13 Topologies)
- LP24 Ladder – classic 4-pole lowpass
- SVF Series – Lowpass, Highpass, Bandpass, Notch, Peak (12 dB/oct)
- Morphing SVF – continuous morph between Low / Band / High
- Formant – 3-band vocal resonator (A–E–I–O–U mapping)
- Advanced Vowel – 5-formant model with Static / Morph / Feedback / Screamer modes
- Comb – tuned delay line with positive / negative feedback
- Phase Filter – multi-stage all-pass (Shepard tone sweeps)
- SEM – state-variable with morphable shape (LP → Notch → HP)
- Multi-Mode Ladder – varislope (6 / 12 / 18 / 24 dB) implementation
Character & Drive
- Pre-Filter Drive: input gain into the filter core
- Character Modes: Clean (Linear), Soft (tanh saturation), Tube (asymmetric shaping), Hard (sine folding)
Chronoweaver Modulation
Generators
8× LFOs
- Shapes: Sine, Saw, Square, Triangle, S&H, Sample & Glide
- Modes: Free (Hz) or Synced (beat division)
- Bipolar / Unipolar switching
4× MSEGs (Multi-Segment Envelope Generators)
- Modes: DAHDSR (classic) or MSEG (drawn)
- MSEG Loop: loop start / end points
- Playback: Envelope (one-shot), LFO Retrig, LFO Sync
- Elastic Time Scale: per-envelope time scale knob (compression / expansion of time)
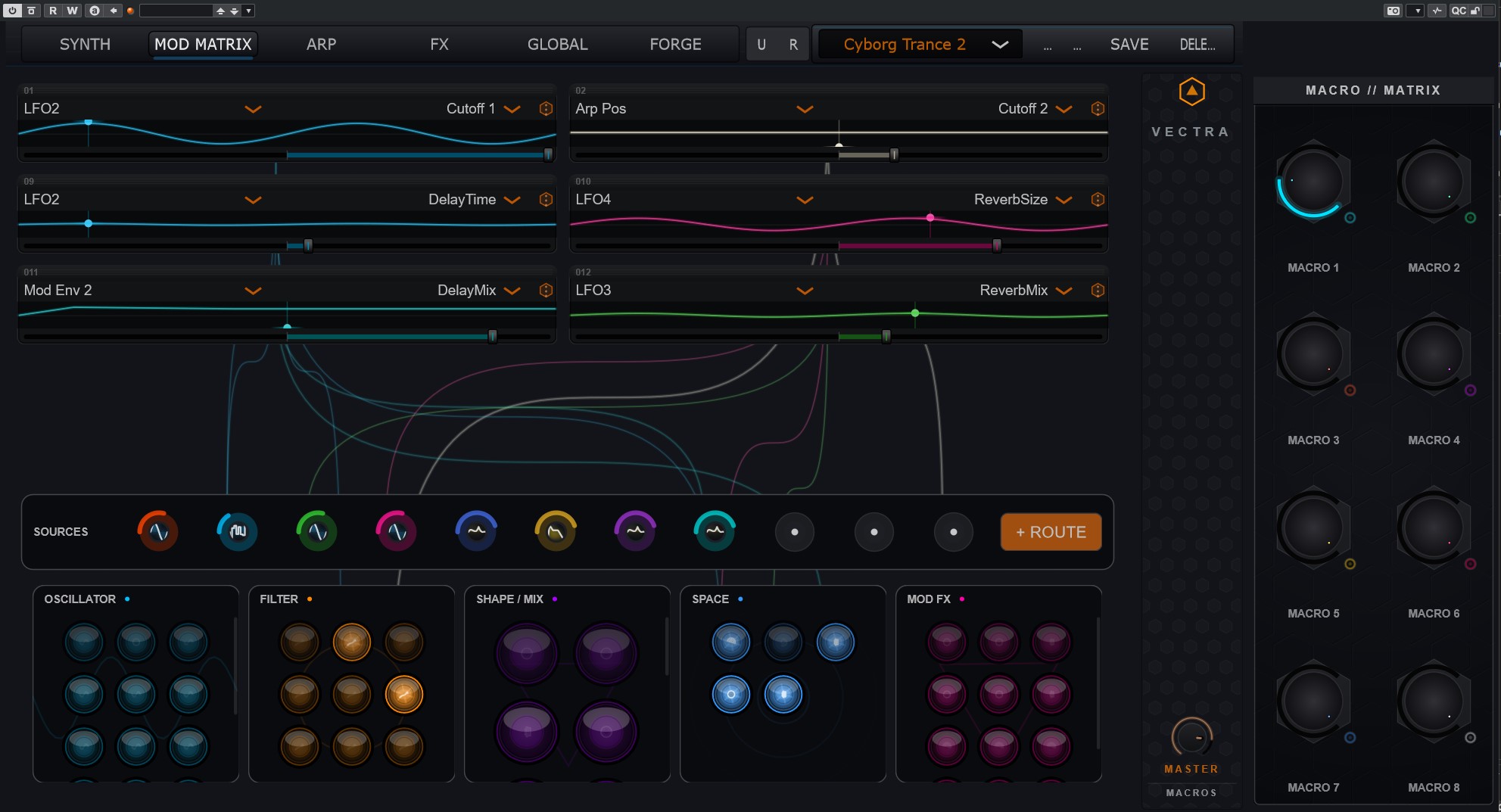
The Living Matrix
- Capacity: 32 modulation slots
- Bi-Directional Workflow:
- Drag & Drop: drag SourceOrb to any modulatable control
- Context Menu: right-click any knob to assign sources
- Visualization:
- Living Cables: animated Bézier curves connecting source to destination
- Pulse: cables glow based on signal intensity
- Modulation Arcs: halo rings on knobs showing modulation range
Master Macros
- 8× Global Macros: renamable, mappable controls for meta-patching
 alt="Living Matrix panel" />
alt="Living Matrix panel" />Maelstrom FX Rack
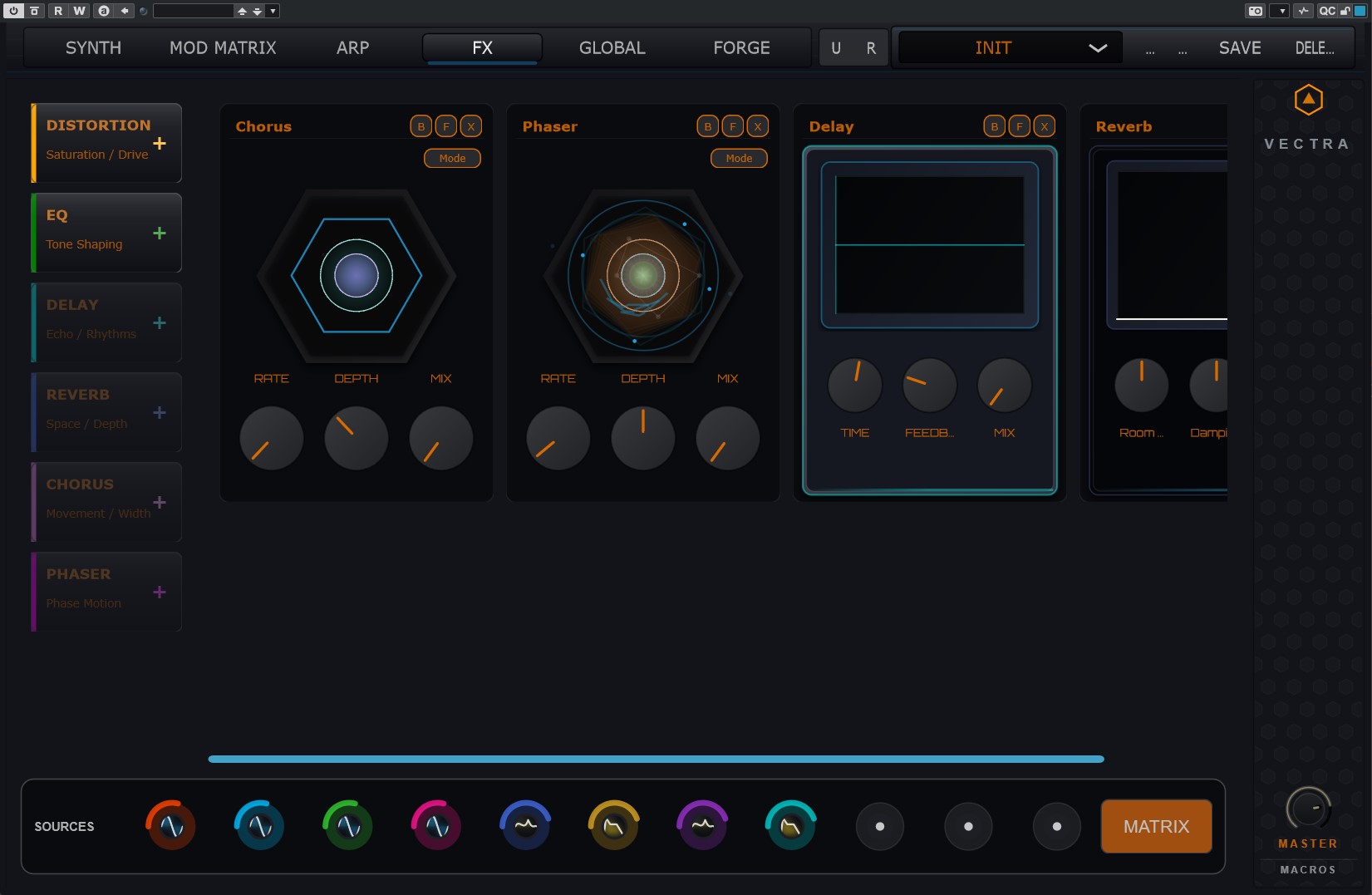
Workflow
- Drag & Drop reordering: modules can be swapped in real time
- Bypass / Focus: individual module toggles
Modules
- Distortion: Tape, Tube, Diode, HardClip, BitCrush, RateReduce, Wavefold – with real-time transfer curve scope
- EQ: 4-band parametric with shelf / peak modes
- Phaser: Rate, Depth, Feedback, Center Freq, Stereo Mix
- Chorus: Rate, Depth, Feedback, Center Delay (turquoise / purple visualiser)
- Delay: Stereo / Ping-Pong, Character (Smear / Saturation), Rhythm tap-division logic, timeline visualiser
- Reverb (E.H.R): Legacy, Event Horizon, Prism, Singularity; Infinite Freeze (∞), Damping, Pre-Delay, Ducking; FFT-based Nebula cloud visualiser
 alt="Maelstrom FX rack" />
alt="Maelstrom FX rack" />Helios & Oculus
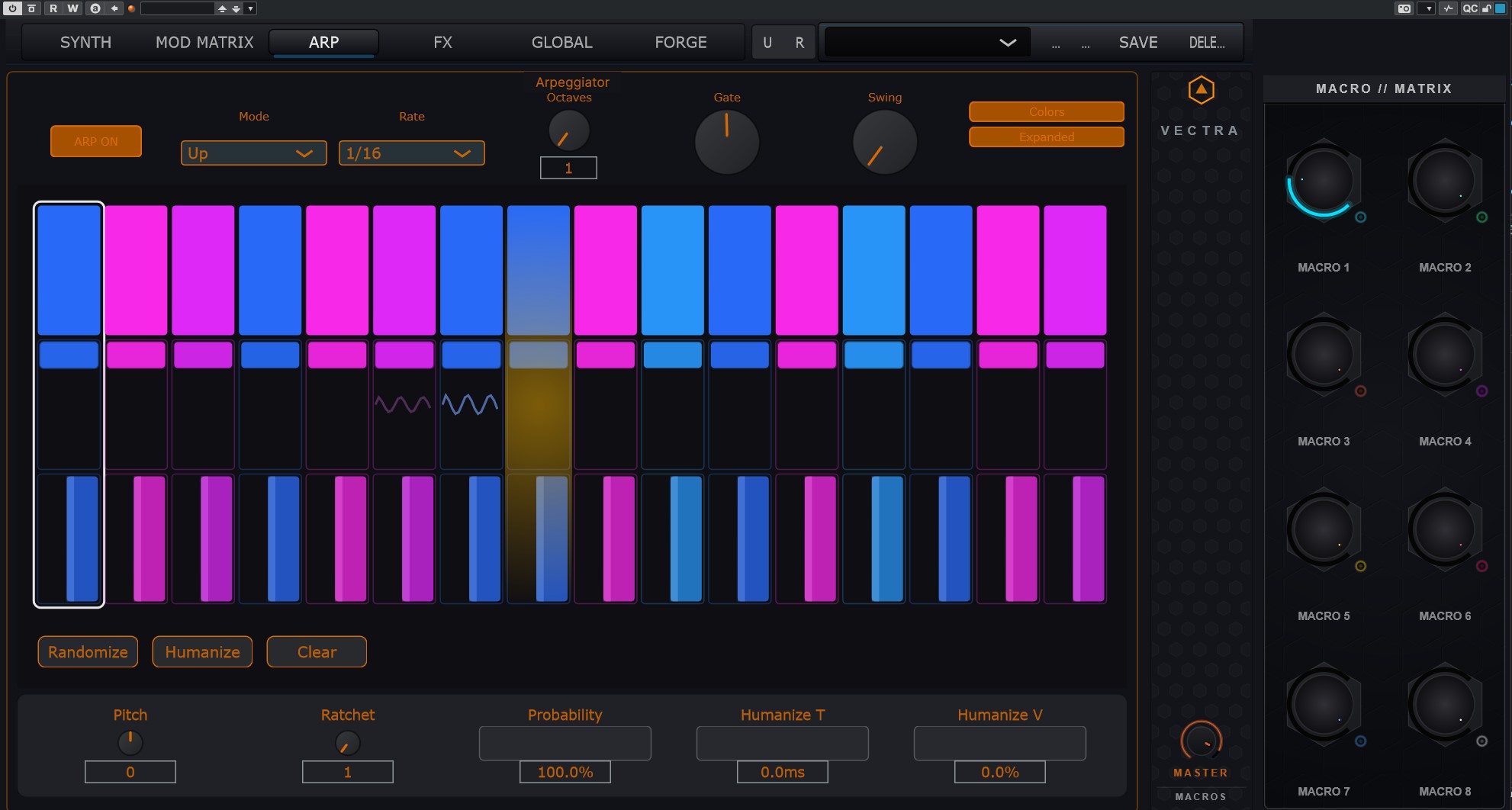
Helios – Probability Arpeggiator
Per-step control for evolving melodic and rhythmic structures.
- Per-step Probability: chance of note triggering (0–100%)
- Per-step Ratchet: sub-divisions per step (glitch rolls)
- Per-step Gate & Velocity
- Per-step Pitch Offset (semitone shift)
- Humanization: timing jitter and velocity drift
- Visuals: Spectrum Mode (colors based on Circle of Fifths)
 alt="Helios Arpeggiator" />
alt="Helios Arpeggiator" />Oculus – Global Visualization
- Mandalizer V2 (The Orrery):
- Layer 1: Living Core (waveform shards)
- Layer 2: Orbital System (unison moons)
- Layer 3: Deep Field (LFO constellations)
- Phase Weaver: hex-clipped goniometer for stereo correlation
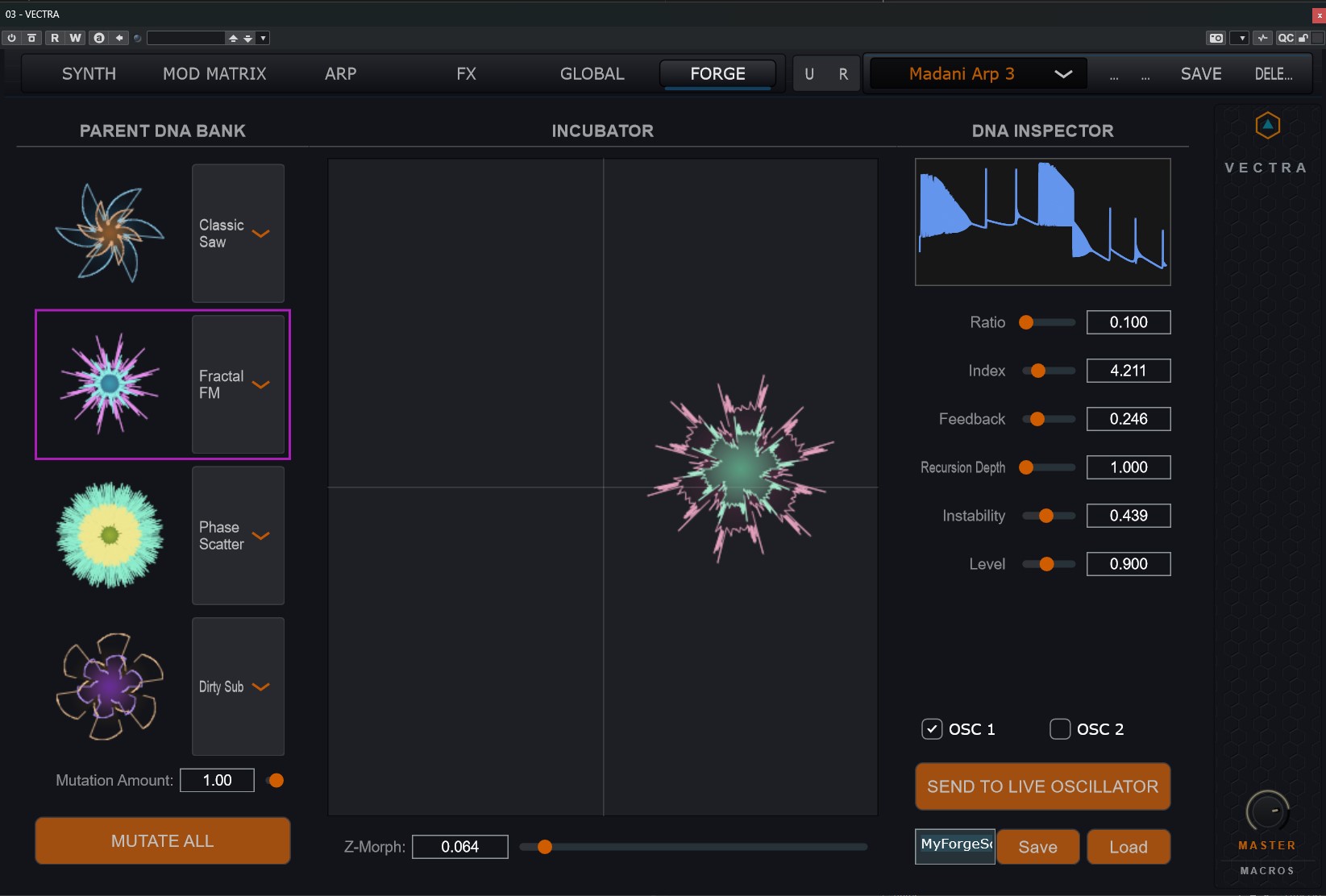
 alt="Forge / visual system" />
alt="Forge / visual system" />Infrastructure
Core Systems
- Preset Management: JSON-based system (.vtrpreset) with category tagging
- License Manager: server-side validation, offline key support, activation overlay
- Oversampling: 1×, 2×, 4× (Ultra) modes
- UI Scaling: vector-based resizing (70% to 200%)
- Safety: DSP_Utils::sanityCheck for NaN / Infinity protection
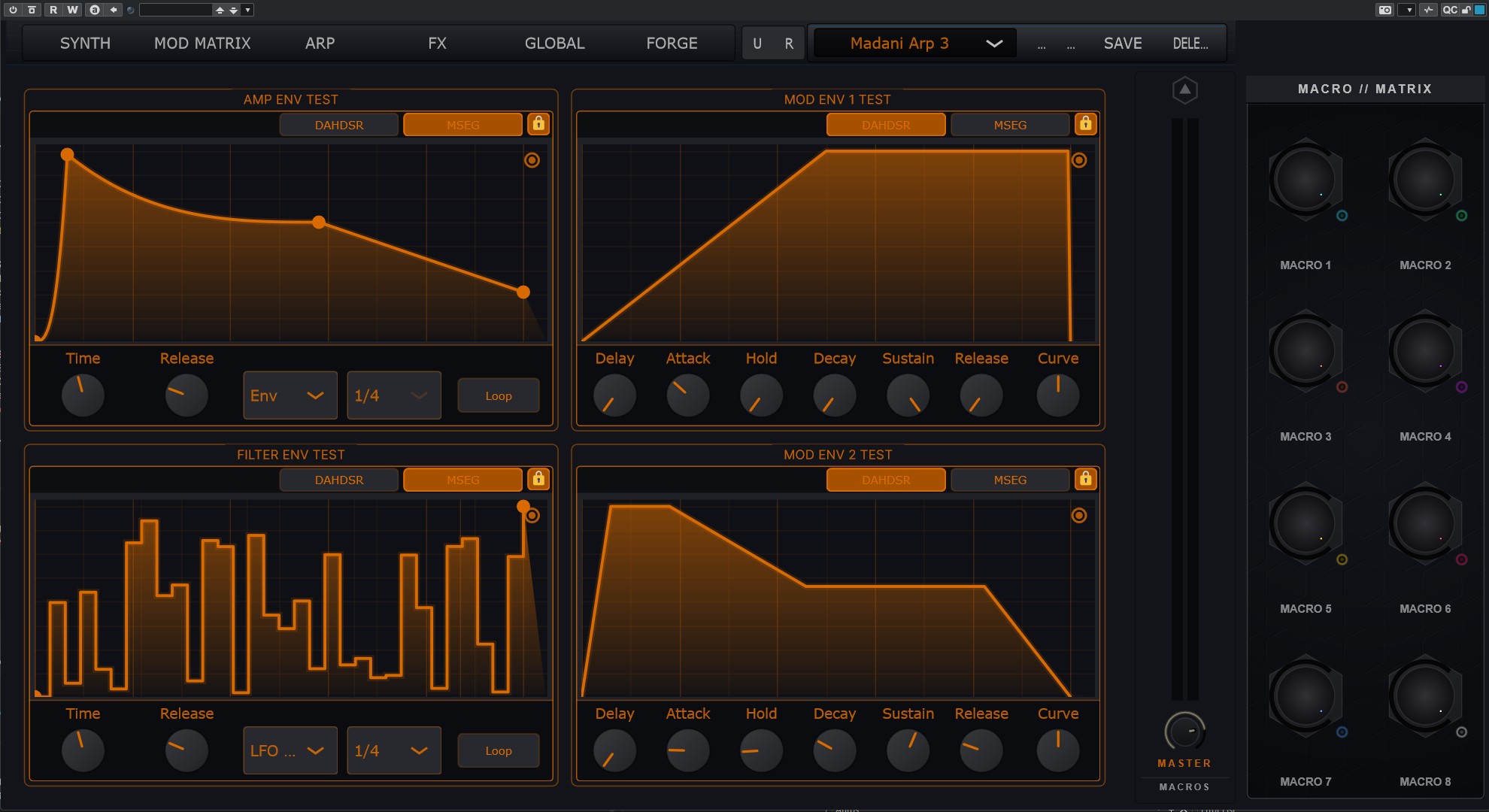
 alt="Envelope / engine detail" />
alt="Envelope / engine detail" />